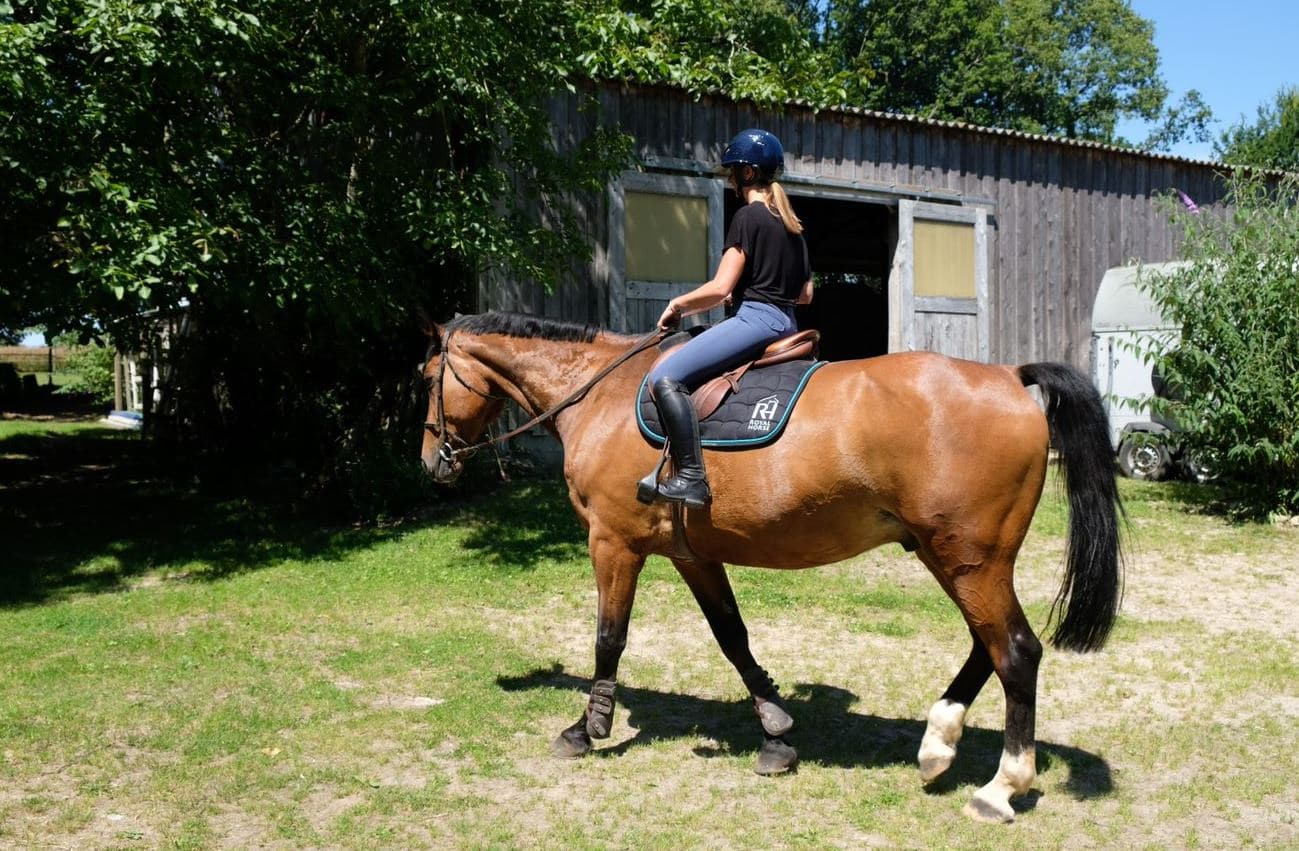
Are you a horse owner or considering becoming one? It is important to know the nutritional needs of your horse. These depend on many factors, including its weight and physical activity. How do you calculate a horse’s energy requirements? What should a horse’s diet include? In this article, we answer all your questions and take a look at horse nutrition.
UNDERSTANDING HFU
Understanding the notion of HFU or Horse Feed Unit is essential to offer your animal a diet containing sufficient energy. Indeed, the energy, provided by the feed, allows to cover different needs of the horse, namely :
- Horse needs : the energy drawn from the feed allows the horse to maintain its vital functions, i.e. to breathe, to eat, to move…
- Production needs: these are needs related to physical activity, growth, gestation or lactation.
The HFU covers the nutritional needs of the horse: it corresponds to the net energy value of one kilogram of raw barley, i.e. approximately 2,200 Kcal.
HOW TO CALCULATE THE NEEDS OF A HORSE ?
You now know what the concept of HFU corresponds to. Let’s see now how to calculate the daily ration to give to your companion. To begin with, it is important to know the average daily needs of a horse according to its weight. You don’t know your horse’s weight? We provide you with an online weight estimation tool.
| Type of horse | HFU per day |
| Pony | 2,1 |
| Saddle horse of about 500 kg | 4,1 |
| Saddle horse of about 600 kg | 4,8 |
| Draft horse of about 900 kg | 6,4 |
The needs indicated in this table correspond to a saddle horse in standard conditions. They may vary according to the horse’s lifestyle. Indeed, a horse in a stable needs a lower energy intake than a horse living in a meadow, because the latter is subjected to more variable temperatures and spends more energy.
HOW TO CALCULATE THE HORSE’S OTHER NEEDS ?
Production needs must be added to maintenance needs to calculate the energy needs of a horse. To do this, you must first estimate the level of effort provided by your horse: very light, light, moderate or intense.
HOW TO ESTIMATE THE EFFORT LEVEL OF HORSES ?
Logic is usually sufficient to estimate the level of effort your horse is putting forth. A horse working only once or twice a week or going out for a few rides is a light effort horse. A horse that is worked more regularly on the flat, say 3 times a week for an hour, is a light effort horse.
If you work your horse more regularly or if you practice a discipline such as jumping occasionally, consider that the effort provided is moderate. Finally, club horses, race horses, or horses that are worked very frequently or go to shows are considered to be high effort horses. Here are some examples of training and their corresponding effort:

- Very light training: occasional walks at a walk
- Light training: work on the flat without jumping or long gallops
- Moderate training: dressage exercises, small to medium rides
- Intense training: show jumping, racing, competition, physical games
To calculate your horse’s needs, always take into account its current level of effort: if your horse works regularly for a short period of time, you will have to increase its ration. If your horse is working regularly for a short period of time, you will need to increase the ration.
As soon as this activity decreases, you will need to reduce the ration gradually. Not sure how much effort your horse is putting in? It is possible to know it with precision by measuring his heart rate during exercise. This calculation allows you to transpose the heart rate into the volume of oxygen consumed, then into energy spent.
HOW TO CALCULATE THE PRODUCTION NEEDS OF A HORSE ?
Now you know how much effort your horse is putting in. To cover all of its energy needs, you will have to add the production needs to its maintenance needs. Here is a table of the number of PDUs to add to the maintenance needs of your companion according to the effort provided :
| Weight in kg | Very light effort | Light effort | Moderate effort | Intense effort |
| 300 | 0,13 HFU | 0,22 HFU | 0,38 HFU | 0,60 HFU |
| 400 | 0,15 HFU | 0,26 HFU | 0,44 HFU | 0,70 HFU |
| 500 | 0,17 HFU | 0,30 HFU | 0,50 HFU | 0,80 HFU |
| 600 | 0,19 HFU | 0,34 HFU | 0,56 HFU | 0,90 HFU |
WHAT ARE THE OTHER NUTRITIONAL NEEDS THAT SHOULD NOT BE NEGLECTED ?
Feeding your horse energy is a good thing. However, it is important to offer him a rich and varied diet, containing all the nutrients necessary for his needs to ensure a good nutritional balance.
WATER
The horse must have clean and fresh water available at all times. A 500 kg horse consumes an average of 30 to 40 liters of water daily. This consumption can increase depending on the temperature, physical activity and age of the horse.
PROTEINS
Have you ever heard of MADC? It is the Digestible Nitrogenous Matter for Horses. It corresponds to the protein needs of your companion. A minimum digestible quantity must be provided to the horse every day. The majority of horse feeds contain MADC values higher than the minimum required, in order to guarantee a good balance between amino acids and proteins.
VITAMINS AND MINERALS
Like all living creatures, horses need to be supplied with minerals in order to stay in shape. These include sodium, trace elements, iron, calcium, phosphorus, copper, iodine and zinc. Vitamins A, B1, B2, B5, B12, D, E, K and PP must also be included in the equine diet, in varying amounts depending on the physiological stage or activity of the horse.
FOOD SUPPLEMENTS
Horses (geldings, mares, stallions) with light physical activity can cover their energy needs with a feed based on fodder supplemented with pellets or flakes with a moderate energy level (0.65 to 0.85 HFU), 85 HFU) On the other hand, horses subjected to intense and repeated efforts require high energy potential feeds to avoid excessive rations and in some cases can be supplemented with specific feeds (joints, feet, preparation for exercise). We invite you to take a look at our feed supplements for Royal-Horse horses: They are developed by veterinarians and nutritionists and will allow you to keep your horse in good health, whatever your objectives.
Estimate your horse’s weight